What is Lyme Disease?
Lyme disease (LD) is an infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi, a type of bacterium called a spirochete (pronounced spy-ro-keet) that is carried by deer ticks. An infected tick can transmit the spirochete to the humans and animals it bites. Untreated, the bacterium travels through the bloodstream, establishes itself in various body tissues, and can cause a number of symptoms, some of which are severe. LD manifests itself as a multisystem inflammatory disease that affects the skin in its early, localized stage, and spreads to the joints, nervous system and, to a lesser extent, other organ systems in its later, disseminated stages. If diagnosed and treated early with antibiotics, LD is almost always readily cured. Generally, LD in its later stages can also be treated effectively, but because the rate of disease progression READ MORE >>
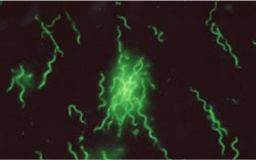
Borrelia burgdorferi
Lyme disease (LD) is an infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi, a type of bacterium called a spirochete (pronounced spy-ro-keet).
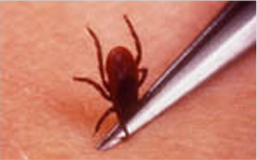
Deer Tick or Black Legged Tick
If you happen to find a tick attached to your skin, watch our tick removal video. Click here to visit our videos page.

Lone Star Tick
Lone Star ticks do not transmit Lyme disease, although they are capable of transmitting other tick-borne diseases.

Dog Tick
In some regions, dog ticks are common vectors for Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever; however, not all bites result in infection.
What is a tick?
Ticks are not insects but Arachnids, a class of Arthropods, which also includes mites, spiders and scorpions. They are divided into two groups – hard bodied and soft bodied – both of which are capable of transmitting diseases in the United States.
Ticks are parasites that feed by latching on to an animal host, imbedding their mouthparts into the host’s skin and sucking its blood. This method of feeding makes ticks the perfect vectors (organisms that harbor and transmit disease) for a variety of pathogenic agents. Ticks are responsible for at least ten different known diseases in humans in the U.S., including Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, babesiosis, and more recently, anaplasmosis and ehrlichiosis.
All About Ticks
Worldwide, there are about 850 tick species and 30 major tick-borne diseases; the U.S. alone has 82 species of ticks collectively causing 10 major diseases listed below:
- Spirochete Transmission by Ticks
- Time to Transmission of Tickborne Diseases: Peer-reviewed Research Papers
- Insights into the development of Ixodes scapularis : a resource for research on a medically important tick species.
- Genomic insights into the Ixodes scapularis tick vector of Lyme disease
- Borrelia burgdorferri is much more infectious in ticks that have taken a blood meal
- The OspA surface antigen protects Borrelia burgdorferri from the inactivating effects of ingested unrelated mammalian antibody as well as promotes colonization in the midgut of ticks.
- Tick Identification chart
- Geographic distribution of different types of ticks in the United States
- Tick Removal Tool
- Where to send ticks to be tested for infection
- Tick Safety
- Seven Ways to Keep Ticks Away From Your Property
Educational Materials
Educational Materials: To achieve its mission, the ALDF provides an array of brochures, tick ID cards and other materials that contain current information on symptoms, diagnosis and treatment guidelines, prevention strategies, and methods of tick-control. Individuals, schools, physicians’ offices, health departments, corporations, and many other organizations may order bulk quantities of these materials for a modest fee. A Spanish language brochure is also available. It should be noted that all of these materials may be downloaded and printed directly from our website.
How to Make Donations and Contributions to Support the ALDF
1) Prevent tick bites potentially leading to Lyme disease or other tick-borne infections,
2) Recognize early symptoms so that potential long-term consequences can be avoided, and
3) Receive quality healthcare from knowledgeable physicians. We promote these objectives by providing reliable and accurate information about risk assessment, epidemiology, symptoms, recommended diagnosis and treatment guidelines, approved and experimental testing methods, prevention strategies, tick-control and much more.
Read MORE>>

